Flash freezing has remained a popular method of preserving foods for transport and long-term storage. In today’s modern food industry, the technologies and equipment involved in frozen food packaging and processing play a pivotal role in ensuring that the food we consume is not only delicious but also safe and nutritious. Let’s have a look at common frozen food processing equipment in the industry today and how they can benefit your production line.
The Evolution and Impact of Freezing Technologies in Food Preservation
Freezing is a food preservation method that has been used for thousands of years. Today’s field of frozen food technologies includes a wide range of tools and methods for food preservation.
As the demand for frozen foods continues to grow worldwide, the technologies and methods behind their preservation will undoubtedly keep advancing, reflecting humanity’s constant pursuit of better, more efficient solutions.
The History of Freezing Foods
Flash freezing is a widely used technique in preserving food. Back in the 1920s, Clarence Birdseye observed the advantages of freezing fish. He realized that faster freezing at lower temperatures resulted in fish that tasted better. In 1925, Birdseye created a machine that quickly froze vegetables for shipping using a pressured brine and water solution. This technology allows producers to sell their frozen products all across the country.

Main Considerations for Technologies and Equipment Involved in Frozen Food Packaging and Processing
Besides considering getting a conveyor belt for the warehouse, you need to explore all the sides when it comes to food freezing processes. For example, did you know there are more than a few ways to categorize modern equipment for freezing? It may generally be separated into two main classes based on how it functions: integrated into the processing line for a continual flow and for freezing the product in batches.
There are three primary categories of freezing equipment, depending on the heat-transfer technique:
- Air-blast freezers – Using swiftly circulating cold air, these freezers efficiently chill the food. They are the most prevalent type of freezer and come in a variety of designs.
- Contact freezers – Conduction is the main mechanism for heat transfer in this process. The food gets frozen when it comes into direct contact with super cold surfaces or when immersed in a chilled liquid.
- Cryogenic freezers – This method leverages liquified gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide to achieve extremely low temperatures.
Based on specific needs, a combination of these three heat-transfer techniques might be employed in unique designs.
Other Two Groups You Need to Be Aware Of
Based on the type of frozen food product, there are two primary groups of equipment. These include Individually Quick-Frozen (IQF) products and packaged products.
Individually Quick Frozen (IQF) items refer to foods where each piece is frozen independently prior to packaging. Popular examples encompass fruits like blueberries and strawberries, vegetables such as peas, corn, and green beans, as well as seafood items like scallops and shrimp. Poultry, including individual chicken pieces and even whole products like frozen turkeys, often undergo the IQF process.
Bulk frozen foods that are packaged prior to freezing are referred to as packaged products. In the frozen food processing industry, various freezing methods are employed. However, for high production rates, systems that seamlessly integrate with packaging operations are favored, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted flow of products.
Key Features of Comprehensive Freezing Equipment Design
Comprehensive freezing equipment, complete with an integrated conveyor belt system for frozen foods and a supplementary conveyor for warehousing, should be meticulously designed. This ensures it caters to every phase of the freezing process, optimizing each component for maximum efficiency.
This involves design for hygienic compliance with safety and sanitation standards and minimizing product loss rates through efficient operation. Additionally, these systems should require minimal maintenance, as this plays a crucial role in the overall cost-efficiency of the operation.

Explore the Advanced Heat-Transfer Methods in Food Freezing Equipment
When considering food-freezing equipment, it’s crucial to recognize the variety of methods available to ensure optimal preservation. The three broad heat-transfer method categories play a fundamental role in the freezing process, each with its unique attributes and applications. Within these techniques, the integration of a conveyor belt for food is vital.
They not only facilitate the movement of products but also ensure a consistent and uniform application of the freezing method. These heat-transfer methods’ specifics can be further broken down into the following categories:
Air-Blast Freezers
These represent one of the marvels of modern food preservation technology. Harnessing the power of fast-moving cold air, these freezers rapidly bring down the temperature of food products, ensuring both safety and quality. Their design allows for the quick and uniform freezing of items, minimizing ice crystal formation and thus preserving the original texture and flavor of the food. Here are different types of this equipment:
- Sharp freezers – are known as blast rooms, and they are essentially cold storage facilities. There usually isn’t any forced airflow, resulting in a slow freezing rate. Instead of processed goods, this machinery is often utilized for bulk materials like beef quarters.
- Tunnel freezers – Cold air flows over the products, which are set on trays or unique spacers. These trays or spacers are either stationary within the tunnel or moved through it on racks or trolleys.
- Belt freezers – single-, multi-, or spiral-belt freezer systems typically use a vertical airflow, forcing cold air through a product layer that’s evenly distributed over the entire belt area. The spiral belt freezer is designed to maximize contact with each product particle. Among the three models, it provides the most versatility in handling a wide variety of products within a limited floor space. Common items processed in these systems include meat patties, fish fillets, cakes, and bakery items. These can be processed in various states—raw or cooked, and either packaged or unpackaged.
- Fluidized-bed freezers – Fluidization happens when food particles, which have relatively similar shapes and sizes (like peas), are exposed to an upward flow of air. Upon reaching a specific airspeed, these particles separate from each other and float in the airstream. This process allows for more uniform freezing of each individual particle.
Contact Freezers
As the name implies, these employ direct contact between the freezing medium and the food product to expedite the cooling process. Unlike methods that rely on air circulation, these freezers achieve rapid temperature reduction through physical touch, ensuring a faster and often more uniform freeze.
This can be particularly advantageous for certain foods where minimizing the formation of large ice crystals is essential to maintaining the product’s texture and overall quality. Here are the types of freezers you can choose from:
- Immersion freezers – These systems use a cooling solution, often made from salt, sugar, or alcohol mixed with water. The product is either dipped into this mixture or sprayed with it as it moves along. This method is commonly used for freezing turkeys and other poultry.
- Plate freezers – Whether oriented vertically or horizontally, regardless of being manual or automatic, plate freezers quickly transfer heat by sandwiching the product between two metal plates.
- Band freezers – These systems are designed to freeze thin layers of products. The product gets shaped and frozen between two continuous stainless steel belts, producing a frozen sheet. Commonly frozen items include fruit purees, egg yolks, sauces, pureed spinach, and other liquid foods like soups.
Cryogenic Freezers
In the initial stages of product development, cryogenic freezing is a beneficial method for rapid low-temperature storage. It’s especially useful for quickly cooling wet, sticky, or delicate products. Once these products are preliminarily set, they can be thoroughly frozen using airflow or contact freezers, which are more suitable for larger-scale operations.
Certain food processing methods utilize cryogenic agents such as carbon dioxide or liquid nitrogen. These agents not only expedite the processes but also minimize damage during production.

Innovations in Frozen Food Packaging Technology: Adherence and Adaptability
Considering the unique requirements of frozen foods, packaging technology in this sector has seen a significant evolution. Depending on their moisture content, most frozen foods can expand by as much as 9%. Thus, packaging material must not only accommodate these volumetric changes but also adhere to stringent FDA regulations for frozen food packaging. The selected packaging should:
- Withstanding freezing temperatures of -40°F.
- Have a food packaging design that offers a good visual appeal.
- Endure the rigors of sealing, freezing, storage, and transportation processes with an industrial conveyor belt.
Use the Appropriate Packaging Materials
In the intricacies of the packaging process, choosing the right material is paramount. As part of the overall system, bulk material handling equipment plays a vital role in efficiently managing and transporting these materials. Here are a few of the materials that are frequently used in packaging:
- Polyethylene (PE) film – This material is durable enough to endure temperatures as low as -40°F, boasts impressive mechanical strength, and is resistant to punctures.
- PE derivatives – Various types of plastics, including shrink wraps, rigid materials, flexible plastics, and single-use packaging, are options for frozen food packaging.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) – This material is resilient to sudden temperature shifts and is typically found in products suitable for microwaving or boiling directly in their packaging.
- Cardboard and laminated paper – Frequently used for fast-moving consumer goods (FMCGs), these packages have a shorter shelf life once removed from the freezer.
- Tin cans – Traditionally, these were used for frozen food packaging. However, compared to newer alternatives, they are not as cost-effective.
- Aluminum foil laminates – These provide optimal performance in terms of water transfer, oxygen permeation, thermal resilience, mechanical stability, and seal integrity.
Ensure the Packaging Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene during the frozen food packaging process is of the utmost importance. Even if freezing stifles microbial growth, it doesn’t eliminate it completely. After thawing, microbial growth will pick up again.
Frozen food producers have various cleaning methods for their packaging lines. Here are some of the most frequently used:
Accordion
- Dry Wipe Down
This method entails cleaning the item and then packaging it using a microfiber cloth while at room temperature.
- Low-Pressure Cleaning
This procedure, often referred to as soft-wash, uses low-pressure nozzles to spray distilled water or other solutions to wash off product and package surfaces.
- High-Pressure Cleaning
Spray nozzles, air dryers, and a setting for hot/cold water are typically included in high-pressure cleaning for frozen food packing machinery.
End of Accordion
Frozen Food Packaging Sealing Technology
Good sealing will ensure the overall safety and quality of the end product by protecting it from the external environment. Based on the specific packaging needs, various methods and packaging machines are at your disposal:
Accordion
- Direct Heat Sealing
This system is versatile and especially suitable for thicker plastic packaging materials, such as polypropylene.
- Impulse Heat Sealing
This system uses an electrical pulse to heat a wire, which then cools down. Impulse heat sealing offers a more budget-friendly option compared to direct heat sealing.
- VFFS Systems
The VFFS packaging system stands for Vertical Forming, Filling, and Sealing technology. It seamlessly integrates the processes of forming the package, filling it with the product, and sealing it, all within a single production line.
- Zip-Locks
This sealing technology is becoming increasingly popular in the frozen food sector due to its enhanced convenience, superior packaging quality, and aesthetic appeal. Frequently, it’s paired with heat-sealing techniques for optimal results.
End of Accordion
Ensuring Quality and Efficiency: The Role of Conveyor Systems in Frozen Food Production
Regardless of the freezing or packaging equipment, frozen food manufacturers need to maintain their food safety and quality standards throughout the process. To achieve this, they require a conveyor system that ensures this superior level of security, minimizing or entirely eliminating product wastage throughout the frozen food production and processing stages.
In most frozen food applications, a bucket elevator and open belt conveyor system can often result in significant product spillage and warming, a severe quality and efficiency concern. Nevertheless, with the use of cable, disc, and tube conveyors, such concerns are mitigated since the product moves within a closed system. Utilizing clear tubing can eliminate the appearance of black specks occurring on the product, which many companies have noticed while using other types of conveyors. Cablevey’s conveyor solutions are specifically designed to address and reduce such challenges.
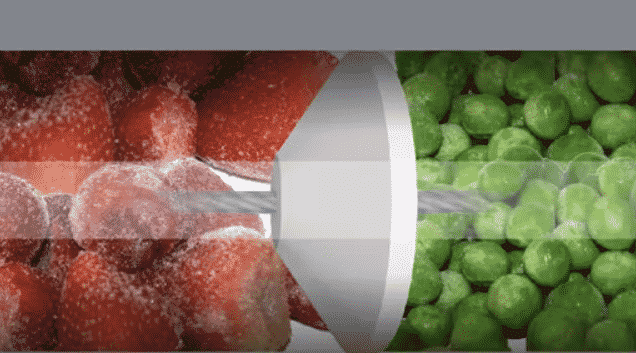
Redefining Conveyor Excellence: Cablevey’s Commitment to the Frozen Food Industry
Cablevey Conveyors has developed frozen food conveyor systems suitable for moving all sorts of food batch ingredients and finished products safely, gently, and in a sanitary manner, no matter the material. These versatile systems can be tailored to accommodate various stages of the production process, from mixing and pretreatment to freezing and packaging, making them suitable for a broad spectrum of applications.
Cablevey’s frozen food conveyor systems will offer you many features and benefits. They come in different sizes and offer a full range of different components to cover any facility layout and conveyor movement needed. If you’d like to know more about Cablevey’s conveyors for the frozen food industry, please contact us.






