Tubular drag conveyors are incredibly versatile and reliable for a wide range of industries. Historically, bulk material handling equipment has been around for approximately fifty years, helping move a variety of delicate materials in different manufacturing processes, most notably in food processing. There are two main types of tubular drag conveyors that we will explore in this blog post – chain and cable drag industrial conveyor belt systems.
What to Consider Before Investing
In order to make the right decision before investing in a new belt conveyor system for your production facilities, there are several factors to consider:
- How tubular conveyors work,
- The differences between chain and cable drag systems,
- How they stack up against other conveyor types,
- How they are used in different production processes.
It is also important to note that tubular drag conveyors can be custom designed based on customer specifications, making them perfect for any business where floor space is limited and the layout is abundant with tight corners and sharp turns. The ultimate guide to tubular drag conveyors will explore everything you need to know to make an informed purchase you won’t regret.

How Do Tubular Drag Conveyors Work?
Tubular drag conveyors are a conveyor belt system that drags bulk materials through an enclosed tube. This tube can be made from plastic, steel, or fiberglass, depending on which industry it is used in. Inside the tubular housing, there is a chain or a cable with evenly spaced solid discs (flights) that push the material forward. The entire system is driven by motor-powered sprockets. The ends of a tubular drag conveyor are connected, forming an endless loop. An important benefit of these systems is that they are completely modular. This means that they can be configured to meet the specific needs of almost any facility.
It’s Ideal as a Conveyor Belt for Food
Additionally, the enclosed nature of the transport makes tubular conveyors ideal for food-grade applications. The risk of product or material contamination is minimized because the tube does not allow for outside particles to enter. Furthermore, the production facility has a very low risk of dust accumulation or dust explosions.
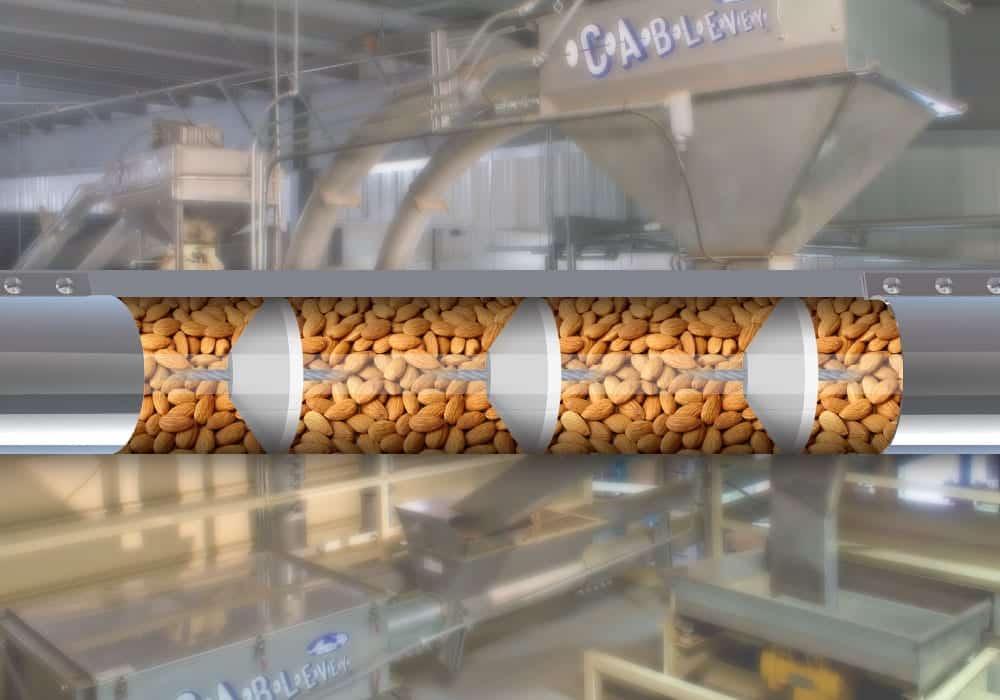
Chain vs. Cable
There are two types of tubular drag conveyors – chain and cable-driven. Chain tubular drag conveyors rely on a series of metal links attached to one another – a chain that moves the solid discs inside the tube. Cable conveyors have a stainless steel cable instead of a chain and are generally more sanitary than chain systems. Both cable and chain conveyors can move approximately 80,000 pounds of product per hour (36,287 kg/h), though this depends on the product bulk density.
Tubular Chain Conveyors
A tubular chain drag conveyor has a stainless or carbon steel chain for moving the material forward inside the tubular enclosure. There are two chain types to differentiate: roller and link chains. Roller chains are made from interconnected plates. Therefore, they allow only one-dimensional movement. Link chains are much more flexible. They can convey products in multiple planes, allowing a single conveyor to transport materials in different directions, depending on the facility’s needs.
The chain, whether roller or link, comes in direct contact with the conveyed material. In food manufacturing, it is imperative that the chain is acid- and corrosion-resistant. It also needs to meet strict FDA sanitation requirements, especially because debris and food particles tend to get stuck between chain pins, plates, and bushing.
Dry cleaning mechanisms and the wet cleaning mechanism that includes a three-step process within the conveyor tube are explained in the table below.
| Type of Cleaning | Mechanism | Description |
| Dry cleaning | Brush box | A line insert with mechanical brushes that brush the material fines off discs. |
| Dry cleaning | Chain knockers | Line inserts that dislodge dirt and debris from the chain by knocking against it. |
| Wet cleaning | Foam cleaner and sanitizer injection | Removes accumulated particles. |
| Wet cleaning | High-pressure water stream | Washes off the foaming solution and the material remains. |
| Wet cleaning | Warm air stream | Blown through the tube, drying the system and preparing it for operation. |
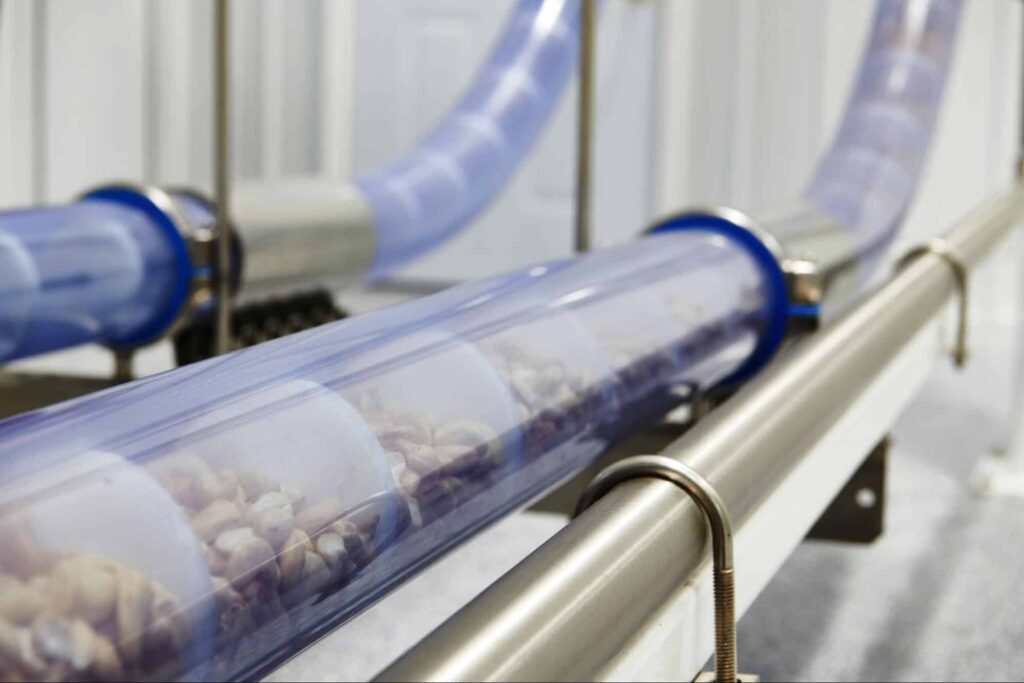
Tubular Cable Conveyors
Instead of a chain, the tubular cable conveyor has a stainless steel cable in charge of moving along the discs and transporting materials. The cable is encased in a nylon jacket, meaning the surface that comes in direct contact with the conveyed product is smooth and doesn’t gather any product particles or debris.
The cable utilized in these systems is of the WSC (wire strand core) type – an incredibly high-tensile cable that is typically used in aircraft. The core of the cable is made from 316 stainless steel surrounded by steel-stranded ropes. You can be sure that it won’t break under normal working conditions. The discs utilized in cable drag conveyors are attached directly to this cable, without any loose parts such as bolts or screws. Therefore, every conveyor component can be easily removed for cleaning and maintenance.
Dry cleaning options and the three-step wet cleaning process for tubular cable drag conveyor systems are explained in the table below.
| Type of Cleaning | Mechanism | Description |
| Dry cleaning | Bristle brush | A special brush for cleaning the inside of tube conveyors. |
| Dry cleaning | Urethane wiper disc | Urethane disc inserts that wipe away material particles from the inside of the tubing while the system is still in operation. |
| Dry cleaning | Brush box | The same type of line insert as in drag chain systems. |
| Dry cleaning | Sponge disc and sanitizing cleaner | A disposable sponge disc for cleaning the inside of the tube with a cleaning agent. |
| Dry cleaning | Air knife | High-pressure air streams that are positioned right where the product gets discharged from the line. Their purpose is to blow away accumulating particles off the discs and the cable. |
| Wet cleaning | Foam cleaning | Cleans the system with foam. |
| Wet cleaning | High-pressure sanitizing rinse | A high-pressure sanitizing rinse that removes accumulated particles. |
| Wet cleaning | Water rinse | Another stream of hot water that washes away the sanitizing rinse, making the system ready for production. |
Conveyor Comparisons
When browsing for the right conveyor solution for your business, it is natural to wonder how each option stacks up against others. The key to selecting the best type of conveyor is understanding its strengths and limitations, as well as how it will interact with your business needs. The following section compares tubular drag conveyors to some of the most popular alternatives.
Similar to the design of drag systems, aero-mechanical conveyors have a steel tube with a circulating rope running through it. The difference is that the discs in this system create a steady airstream by moving at incredibly high speeds within the tube.
You may think that moving at higher speeds results in higher throughput. That is true, but in delicate material transport, high speeds equal high product degradation. Thus, for conveying fragile products, aero-mechanical systems need to maintain slow and steady speeds, ultimately not making them any more efficient than tubular drag conveyors. Another downside to aero-mechanical conveyors is that they require rope-tensioning. This prolongs downtime and adds another maintenance step that could lead to higher costs.
At first, you might think that the differences between the belt and tubular drag systems cannot be more obvious. The former is an open system with motor-driven pulleys moving a closed belt loop in one direction, and the latter is a closed system with a tube, chain or cable, and discs. However, a belt conveyor can also be closed, bringing it closer to a tubular conveyor design.
Unfortunately, closed belt conveyors lack the flexibility of tubular drag systems. As a result, they are not good at vertical material transport, making them a poor choice for restricted spaces or steep inclines. Belt systems are also incredibly expensive in the initial phase. Overall, for food processor needs, they are not the best choice.
Bucket conveyors have horizontal drums that are lifted by a motor or a drive shaft and lowered onto the material to be conveyed. The buckets then rise on an incline, collecting the products as they go. These solutions typically convey materials vertically, but they can also do so horizontally at times. They are a good option for transporting friable materials.
The main disadvantage of bucket elevators is that they have many moving parts (nuts, bolts, buckets, etc.) that make them difficult to maintain and clean. They are a good choice for transporting fertilizer, grain, and similar bulk materials but cannot meet sanitary regulations as well as tubular drag conveyors.
Pneumatic conveyors include air pressure conveyors and vacuum conveyors. Both utilize different pressure conditions (negative in the case of vacuum and positive in the case of air pressure conveyors) to transport material. They are optimal systems for the following materials:
- Coal fines,
- Food products,
- Metal powders,
- Sands,
- Starch,
- Sugar, and more.
Similar to aero-mechanical systems, pneumatic conveyors are not the gentlest. They can damage up to 10% of the conveyed product! This is a liability that food manufacturers are not willing to take. Compared to tubular drag conveyors, pneumatic systems also use a lot of electric power. A pneumatic vacuum conveyor generates considerable noise as well, which can become a health hazard for employees.
Screw conveyors (also called auger conveyors) consist of a screw-like blade that rotates inside a tube. These rotations allow the material inside the tube to move. These systems are a good choice for moving food waste, meat, boiler ash, animal feed, municipal solid waste, and other semi-solid materials. They are less than ideal for fragile material transport because the rotating blade causes product breakage, grinding, and blend separation.
Moreover, screw augers are not nearly as flexible as tubular drag conveyors. Their use in multiple planes is restricted mostly because of the upward motion and design of the helical blade. The degree of incline of screw conveyor systems determines how much energy they use. Screw systems set up on a high incline will have a high energy consumption, especially compared to tubular cable drag conveyors that don’t need much horsepower to operate.
Cable vs. Chain Drag Conveyors
At the end of this extensive comparison, we should highlight the main differences between the cable and chain tubular drag conveyors. From what we described before, you may feel that they are similar and that it doesn’t matter whether you choose one or the other. In fact, the opposite is true. Here is why you should pay close attention to whether you invest in a tubular cable or chain drag conveyor.
The Main Difference – The Cost
The initial investment in both of these tubular drag system types is in the medium range. When it comes to long-term costs, however, the prospects are quite different. Tubular chain conveyors require high maintenance costs because they need more frequent maintenance than cable conveyors. Round-link chain systems are the most demanding – because their sprockets tear up often, businesses face high replacement costs and extensive downtime. Operating costs are also higher with chain systems because they require more powerful motors to run (more horsepower).
Food Safety
Another significant difference is in the sanitary compliance of these two tubular drag system types. They are both enclosed and ensure protection against foreign contamination, but they are not equally easy to clean. Chains have more of their surface area in direct contact with the conveyed product. As a result, food residue and particles gather in the connections of the chain, becoming a breeding ground for bacteria. These areas are challenging to clean and sanitize.
On the flip side, cables are sealed in nylon, making them smooth to the touch. It doesn’t have any components or crevices where product particles could collect and potentially become a safety hazard. To ensure that your facilities are in strict accordance with the food safety guidelines, you are better off with a tubular cable drag system instead of a chain one.
Cleaning Protocols
Both chain and cable drag conveyors have wet and dry cleaning mechanisms. As outlined above, cable systems have more options available than chains, making them easier to keep clean and sanitized for safe operation.
The Difference Is in Strength, Too
Finally, cables are approximately 25% stronger than chains. The type of cables used in tubular cable systems can also be found in aircraft, bridges, cranes, and elevators. If you are looking for something sturdy and reliable, you cannot go wrong with a cable conveyor.

What Kind of Materials Do Tubular Drag Systems Move?
All the different materials that these conveyors transport all across the world can be roughly sorted into four categories:
- Fragile materials – These materials cannot withstand being transported by other conveyor types. They typically include fragile fruit, breakfast cereals, snack foods, vegetables, pasta, and similar food products.
- Clean materials – If a product needs to be kept at a specific sanitary level, it should be protected from outside influences. A tubular drag conveyor is perfect for that.
- Toxic materials – Hazardous materials such as industrial powders and manufacturing side products need to be transported in a contained manner. Products that pose the risk of explosion or chemical contamination also need to be conveyed in an enclosed space.
- Small and powdered materials – The main concern with materials that can be blown away is material loss. Tubular drag conveyors prevent this with their tubular design.
In general, tubular drag solutions are great for bulk materials.
The table below shows an overview of what they can safely transport in various industries.
| Industry / Application | Materials | Notes |
| Coffee | Roasted beans, green beans, ground coffee, freeze-dried coffee, coffee with sugar and creamer | Tubular drag cable conveyors protect materials from degradation, with minimal grinding and breakage |
| Nuts | Walnuts, pine nuts, pistachios, hazelnuts, cashews, nut mixes | Cable drag material handling solutions can be used in all sections of nut processing plant (sorting, roasting, chopping, and packaging) |
| Snack foods | Pop chips, cookies, popcorn, trail mix, crackers, dried fruit | Tubular drag conveyors preserve material and product integrity, offering a better choice than belt conveyors, bucket elevators, pneumatic conveyors, and screw augers |
| Pet food | Seeds, nutrients, kibble, pellets | Tubular drag cable systems provide gentle and sanitary transport for all forms of pet food |
| Breakfast cereal | Puffs, extruded ingredients, flaked cereals, finished cereals | Drag conveyors can be used in every step of the cereal production process |
| Specialty grains and foods | Oilseeds, malt, industrial hemp, grain blends, vegetables, fruits, beans | All sizes, weights, and combinations of grains can be transported with tubular cable drag solutions |
| Powders | Food ingredients, industrial powders, blends | The Cablevey 6″ diameter conveyor is best for moving powders, transporting up to 45,000 pounds of powder per hour without damaging the product |
| Industrial materials | Plastics – fluff, flake, pellet, powdered,Biomass – wood pellet | Tubular drag conveyors reduce the heat and friction usually associated with transporting these materials |
The Advantages and Applications of Tubular Drag Conveyors in Various Industries
Tubular drag conveyors are transport systems of the future. They are easily customizable, quiet, energy-efficient, gentle on the materials, and easily cleaned and maintained. Their main benefits include ensuring a dust-free environment and protecting the materials from cross-contamination. Between the two tubular drag conveyor types, cable conveyors are the definite frontrunner in the food processing industry.
These solutions are used in a wide variety of sectors, but primarily for transporting coffee, snack foods, pet food, nuts, breakfast cereal, powders, specialty foods and grains, and industrial materials that cannot be conveyed otherwise. Not every conveyor system is meant for every industrial purpose.
But if you feel that your business could benefit from such a solution, please don’t hesitate to reach out to Cablevey Conveyors. Our products are running in over 60 countries worldwide, and we’d love to help make your production facilities as cost-effective as they can be!
FAQ
What Are the Key Benefits of Tubular Drag Conveyors?
Tubular drag conveyors are customizable, quiet, energy-efficient, and gentle on the materials. They can be easily cleaned and maintained, and they help ensure a dust-free environment while protecting the materials from cross-contamination.
Which Industries Primarily Use Tubular Drag Conveyors?
Tubular drag conveyors are used in a wide variety of sectors, but they are primarily used for transporting coffee, snack foods, pet food, nuts, breakfast cereal, powders, specialty foods and grains, and industrial materials that cannot be conveyed otherwise.
What Is the Difference Between Drag Chain Conveyors and Cable Conveyors?
Both are types of tubular drag conveyors, but cable conveyors have been identified as the frontrunner in the food processing industry due to their gentle handling of food products and efficient operation.
Can I Customize a Tubular Drag Conveyor for My Specific Needs?
Yes, our custom conveyor belt for a warehouse or any other processing is highly customizable to suit specific transportation needs and the unique conditions of your production facilities.
I Am Interested in a Tubular Drag Conveyor Solution for My Business. How Can I Get in Touch With Cablevey Conveyors?
You can reach out to Cablevey Conveyors through our contact page on their website. We have products running in over 60 countries worldwide and are dedicated to making your production facilities as cost-effective as possible.






